Coach Solutions, ClassNK to Streamline Verification of Vessel Emissions Data

Coach Solutions, a Kongsberg Company, and classification society ClassNK have partnered to deliver an automated emissions data verification process for their mutual clients.The companies said the process creates a seamless experience for shipowners and Document of Compliance holders who need to extract, standardize, verify and share vessel data for transparent use by stakeholders.The integration with ClassNK is a strategic partnership that, from January 2026, will further strengthen Coach’s mission to put practical…
Container Ship Emissions Remain Steady

In its latest quarterly analysis, VesselBot analyses 73,353 container ship voyages completed by 4,750 vessels between July and September 2025, revealing that total container ship emissions reached 50.3 million tons in Q3 2025, remaining virtually unchanged (-0.2%) compared to Q3 2024 despite a 2.3% increase in voyages.Average well-to-wake emissions intensity improved to 195.9 g CO2e/TEU km, down 1.6% year-over-year, driven by longer steaming times and reduced port dwell times.Direct China-U.S.
UN Shipping Emissions Levy Deal Sets Stage for US-EU Clash

The International Maritime Organization will meet this week to formally decide whether to impose a carbon emissions price on global shipping, a move supported by an EU-led bloc including Britain, China and Japan but strongly opposed by the U.S.The IMO struck a preliminary deal to charge the global shipping industry for emissions in April after the U.S. pulled out of associated talks, prompting Washington to threaten "reciprocal measures" against any fees charged on U.S. ships.The…
Ferry Owners Face 'Double Taxation' from EU, Interferry Warns

Interferry called on the European Commission to immediately harmonize its unilateral EU ETS / FuelEU Maritime regulations with the recently agreed IMO Net-Zero Framework, warning that failure to align Greenhouse Gas regulations will lead to double payment for emissions."We cannot have a situation where operators are paying twice for the same emissions. The European Commission pledged to align its rules once a strong global framework was established at the IMO," said Johan Roos, Director of Regulatory Affairs at Interferry. "That framework is now in place.
Onboard Carbon Capture Lifecycle Assessment Highlights Savings
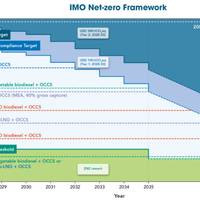
A life cycle assessment (LCA) conducted by the Global Centre for Maritime Decarbonisation (GCMD) has quantified onboard carbon capture’s potential to provide GHG emissions savings.The study provides an in-depth analysis of GHG emissions and costs associated with onboard carbon capture systems (OCCS) across the entire carbon value chain, accounting for emissions from fuel production, transport and use, to CO2 capture onboard the vessel and its final disposition.The deployment of…
Mediterranean ECA Effective May 1
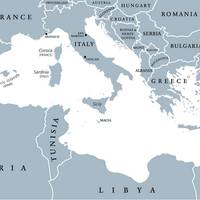
The Mediterranean Sea Emission Control Area (ECA) for sulphur oxides enters into effect on 1 May.This will make the Mediterranean Sea the fifth ECA for sulphur oxides in the world.In the Mediterranean Sea, it means ships will have to use marine fuel with lower sulphur content, down from 0.5% (a global requirement) to a maximum of 0.1%.Sulphur oxide emissions lead to sea and land acidification and contribute to fine dust, which is linked to respiratory and cardiovascular conditions.Sulphur oxide emissions in the EU have decreased by approximately 70% since 2014…
UN Shipping Agency Strikes Deal on Fuel Emissions

Countries at the U.N. shipping agency struck a deal on Friday on a global fuel emissions standard for the maritime sector, which will impose an emissions fee on ships that breach it and reward vessels burning cleaner fuels.The U.S. pulled out of the climate talks at the International Maritime Organization in London this week, urging other countries to do the same and threatening to impose "reciprocal measures" against any fees charged to U.S.
Wood Mackenzie: LNG for Power Generation Emits 'Significantly' Less Than Coal
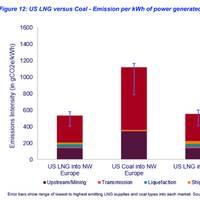
Wood Mackenzie has published a new report comparing the life cycle emissions of LNG with those of coal for power generation, finding the combustion of coal is related to significantly higher emissions.Wood Mackenzie’s analysis in the report titled 'Shining a light on the ‘coal versus LNG emissions’ debate' reveals the lifecycle emissions of U.S. LNG are typically around 48% of the coal equivalent. This difference is not just related to the significantly higher emissions related…
Danelec Launches Emissions Compliance Module
Danelec launched an new vessel Emissions Compliance Module, offering shipowners and operators a way to meet stringent environmental regulations while reducing administrative burdens and improving fleet performance.Danelec’s Emissions Compliance Module allows shipowners and operators to transfer emissions data to class societies and third-party verifiers, simplifying compliance with regulations including EU Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV), UK MRV, IMO Data Collection System (DCS)…
North Atlantic ECA Plan to be Submitted to IMO
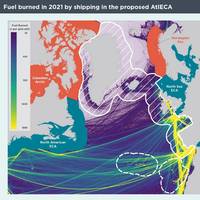
A new study published by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) indicates that up to 4,300 premature deaths can be avoided by an emissions control area in the North Atlantic. The economic benefits of this health benefit could amount to as much as €29 billion ($31 billion).As part of an international coalition that has already contributed to the establishment of an Emission Control Area (ECA) in the Mediterranean, NABU is committed to an ECA in the North Atlantic (AtlECA) and plans to submit a proposal to the IMO Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC) in spring 2025…
Exhaust-sucking Barge to Capture Ship Emissions in the Port of Los Angeles

STAX Engineering announced it has secured a five-year contract to deploy its cutting-edge emissions capture services at Shell’s Mormon Island Terminal in the Port of Los Angeles, coinciding with new California Air Resources Board (CARB) emissions regulations. STAX’s emission capture and control solution offers an alternative to shore power for emissions reduction for tankers. Available as a land- or barge-based solution, the mobile, flexible exhaust capture system is designed to fit all ships without modification…
Call for North Atlantic Ocean ECA
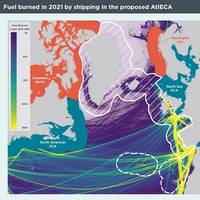
Recent research into the impact of an Emissions Control Area (ECA) in the North Atlantic Ocean confirms that there would be significant emissions reductions benefits if such an area were to be established, says environmental organization Opportunity Green.The North Atlantic Emissions Control Area would mean stricter regulations on ships in designated areas, aimed at reducing and controlling their emissions of SOx, fine particulate matter (PM2.5), and NOx.The International Council…
Cleaner Shipping Fuel is Contributing to Ocean Warming, Scientists Say

Shipping fuel regulations introduced in 2020 have led to a substantial cut in sulphur dioxide (SO2) pollution, but may also have made the ocean warmer by reducing cloud cover, according to a modelling study in a paper published late on Thursday.International Maritime Organization (IMO) rules to tackle marine pollution forced shippers to cut their fuel sulphur content to 0.5% from 3.5%, leading to an 80% decline in SO2 emissions, according to a research team led by Tianle Yuan at the University of Maryland.SO2…
Red Sea Dissruptions Are Driving Up Carbon Emissions

A surge of attacks on ships traveling the waters of the Red Sea is forcing shippers to reroute their vessels, sending them on longer journeys that drive up their carbon dioxide emissions.For companies struggling to account for – and lower – the climate-warming emissions associated with their businesses, these rerouted journeys add to the challenge. Many companies had already revamped their supply chains as they navigated COVID-19 disruptions, extreme weather risks, trade protectionism that forced them to change suppliers…
Red Sea Crisis Forces Operators to Use More Containerships, Adding to Emission Concerns

The shipping industry's pledge to limit its carbon footprint may suffer a setback as the current Red Sea crisis prompts it to use more vessels and take longer routes to ensure the smooth sailing of global maritime trade.Iranian-backed Houthi militants' attacks on vessels passing through the southern Red Sea have choked trade through the Suez Canal, driving many container shipping companies to add 10-14 days to the voyages between Asia and Europe and add more vessels.The disruption…
IMO Approves Two New Emission Control Areas

The IMO’s Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC 81) approved the establishment of two new Emission Control Areas (ECAs) in the Arctic when it met last week.The ECA in Canadian Arctic Waters is for nitrogen oxides, sulphur oxides and particulate matter. The Norwegian Sea ECA is for nitrogen oxides and sulphur oxides. The ECA proposals will now be submitted to MEPC 82 for adoption.“The creation of these two new Emission Control Areas will set an important precedent for protection of our climate and our ocean…
Pressure Builds for Charge on Shipping Sector's CO2 Emissions

The European Union, Canada, Japan and climate-vulnerable Pacific Island states are among 47 countries rallying support for a charge on the international shipping sector's greenhouse gas emissions, documents reviewed by Reuters showed.The documents, being discussed at an International Maritime Organization (IMO) meeting now entering a second week, outline four proposals with a combined 47 backers for imposing a fee on each tonne of greenhouse gas the industry produces.Support for…
Maritime Emissions Reduction Center Launched in Athens

The Lloyd’s Register (LR) Maritime Decarbonization Hub is collaborating with five leading shipowners as founding members in the establishment of a not-for-profit Athens-based global Maritime Emissions Reduction Center (M-ERC) that will focus on optimizing the efficiency of the existing fleet.The M-ERC is being created with the goal of removing technical, investment and community barriers for the uptake of solutions to reduce the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of the existing global fleet…
Gasum to Manage Wasaline’s Emissions Allowances

Finnish state-owned energy company Gasum has been selected by shipping company Wasaline to manage its EU Allowances (EUA) portfolio.The partnership will enable Wasaline to better predict and manage the costs of its emissions allowances, according to the company.The EU emissions trading system has included the maritime sector since the beginning of this year.Outsourcing their emissions trading and EUA portfolio allows shipping companies to both manage and predict their costs.Gasum…
New Tech to Monitor a Ship's Black Carbon Emissions

Green Instruments A/S and Danish Technological Institute have developed a real-time flue gas sensor technology - The Extinction-Minus-Scattering (EMS) measurement method - to accurately measure black carbon emissions from ships, a tech which could be instrumental in meeting increasing regulatory demands of the shipping industry for black carbon emission standards. The EMS method enables real-time in-situ measurement capabilities, traceability, and lowered ownership costs, tackling…
World's Largest Cruise Ship Sets Sail, Bringing Concerns About Methane Emissions
The world's largest cruise ship is set for its maiden voyage on Saturday, but environmental groups are concerned that the liquefied natural gas-powered vessel - and other giant cruise liners to follow - will leak harmful methane into the atmosphere.Royal Caribbean International's Icon of the Seas sets sail from Miami with capacity for 8,000 passengers across 20 decks, taking advantage of the surging popularity of cruises.The ship is built to run on liquefied natural gas (LNG), which burns more cleanly than traditional marine fuel but poses greater risks for methane emissions.
BSM Geared to Go on Carbon Compliance Management

With only a few days to go until EU’s Emission Trading System (EU ETS) kicks in for the shipping industry from 2024. Bernhard Schulte Shipmanagement (BSM) reportes it has developed a comprehensive range of carbon compliance and EU ETS management services designed to support owners and operators mastering the complex regulation requirements and to reduce their carbon footprint and related costs.“Our approach not only encompasses EU ETS management and compliance services but also seeks to optimise ship and fleet performance to reduce CO2 emissions and financial exposure…
AIP for SDARI Ship Designs

ClassNK awards AiPs for SDARI’s green fuels powered vehicle carriers for ammonia ready LNG dual fueled 7,000CEU, and both methanol/ammonia dual fueled 10,000CEUClassNK has issued Approvals in Principle (AiPs) for three vehicle carrier designs developed by Shanghai Merchant Ship Design & Research Institute (SDARI). The first AiP acknowledges an ammonia ready LNG dual fueled vehicle carrier with a capacity of 7,000 CEU, a significant first in China’s independently developed design.









